Differential-pressure method and equal-pressure method are the commonly used test methods in film permeability testing. Empirical tests have proved that differential-pressure method and equal-pressure method are two completely different test methods.
1. Analyses of Test Principles
1.1 Differential-pressure method
Vacuum method is the most representative one in differential-pressure method, and it is also the definition method of gas permeability testing. In this method, (see fig. 1) permeation cavity is divided into two independent parts by sample package. Evacuate these two parts and then fill one side with test gas of 0.1Mpa (absolute pressure) while keep the other side in vacuum state. In this way, a pressure difference of 0.1Mpa forms on two sides of the specimen. Test gas transmits through the film into low-pressure side and then causes a pressure change there. With the pressure variation tested by high precision vacuum gauge, gas transmission rate (GTR) can be calculated according to the formula.
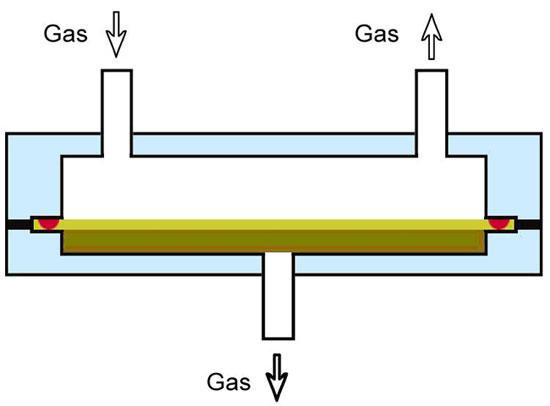
Figure1. Test Principle of Differential-pressure Method
Differential pressure method has no selectivity to test gas. It is low in test cost and high in test efficiency. The most salient feature of this method is that the gas is pure in the test environment. In vacuum method, the whole test chamber is evacuated to below 27Pa and then the upper chamber is filled with pure test gas. In this way impurity gases (non-test gas) of the whole test environment can be neglected. Correspondingly, the effect of these impurity gases can be eliminated.
1.2 Equal-pressure Method
At present, sensor method is the main method employed in gas permeability testing using equal pressure method. It is mainly used for oxygen permeability testing. The test principle is shown in figure 2 below: permeation cavity is divided into two independent airflow systems by the specimen with one side being the flowing testing gas (pure oxygen or mixed gas of oxygen) and the other side being flowing dry carrier gas (nitrogen gas). Pressure of the two sides is equal but oxygen partial pressure is different. Under the function of oxygen concentration difference, oxygen transmits through film and is diverted into the sensor by nitrogen carrier gas. With the oxygen permeance measured by the sensor in nitrogen carrier gas, oxygen gas transmission rate (O2GTR)of the package can be calculated.
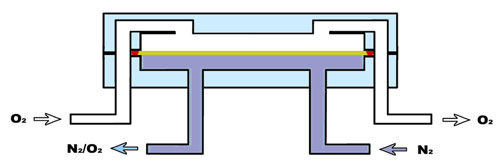
Figure2. Test principle of differential-pressure method
The prominent advantage of equal-pressure method is its ability to test package oxygen permeability. However, its application is not as broad as differential-pressure method in terms of test gas. Due to the adoption of carrier gas in equal-pressure method, there are two kinds of gases existing in the system. On two sides of the specimen, in addition to an oxygen partial pressure of 0.1MPa, an equivalent partial pressure of nitrogen gas with opposite direction of gradient is also there. Therefore, in equal-pressure method, when oxygen gas transmits through film, nitrogen gas transmits reversely at the same time.
2. The Influence of Reverse Transmission of Nitrogen Gas in Equal-pressure Method
2.1 Principle of Diffusion
Macroscopic diffusion is the migration of certain portion of matters resulting from microcosmic collision of the matter. The diffusion happens because molecules moves from a region in which they are highly concentrated to a region in which they are less concentrated. When there is only one kind of matter existing, diffusion is caused by intermolecular collision and such diffusion is defined as self diffusion. If there is more than one kind of molecules moving, molecule collision results in the diffusion of each material and such diffusion is defined as interdiffusion. In the latter one, the collision process itself does not distinguish molecule type. Therefore number of matters participating diffusion can affect diffusion speed to some extent. Consequently, the coefficients of interdiffusion and self diffusion differ.
2.2 Diffusion Model of Gas Permeability Test Method
According to previous discussion, it can be seen that as to vacuum method (differential-pressure method), diffusion is single gas in one direction during the whole test process, thus it is self diffusion, which can be described with the Fick law. While in equal pressure method, there are two kinds of gases diffusing in opposite directions, thus is interdiffusion, which is caused by the reverse transmission of nitrogen gas from lower testing chamber to upper testing chamber. Correspondingly, the influence of interdiffusion should be considered in evaluating barrier property of materials.
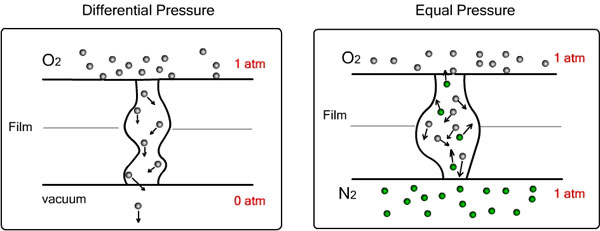
Figure3. Diffusion Model of Differential-pressure Method and Equal-pressure Method
2.3 The Influence of Inverse Transmission of Nitrogen Gas in Equal-pressure Method
When mixture gases are adopted in equal-pressure method, the whole diffusion model will be more complicated. And it becomes more difficult to quantify diffusion coefficient of every matter. Here we can suppose there are only two kinds of gases in the model of equal-pressure method, that is, test gas is pure oxygen and carrier gas is high pure nitrogen gas. The diffusion model can be constructed as below:

Figure4. Illustration Model of the Two Diffusion Flow
We assume that 1 is for oxygen gas and 2 for nitrogen gas, the diffusion of these two gases are described as follows:
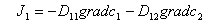
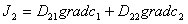
D12gradc2 and D21gradc1 are the coupling flow produced by coupling effect
With the reciprocal relation of Onsager we can know:
D12=D21
D11D22≥D122
This relation is the so called ‘slow down the quick ones and speed up the slow ones ’ that we commonly say, where D12=D21<0. Therefore, no matter how the concentration gradient is, the influence of coupling flow cannot be neglected. At present, the research on interdiffusion still focuses on the combination of specific coupling matters and specific diffusion environment, either of which will affect interdiffusion coefficient. Moreover, there is no unified principle to follow.
Diffusion is only a part of the whole transmission process. The existing of multiple transmission mediums will not only affect the process of diffusion, but also the processes of solution and adsorption. It is obvious that nitrogen gas in equal-pressure method affects the whole transmission process of oxygen. That is why equal pressure method differs with differential pressure method in nature.
3. Conclusion
In conclusion, both differential-pressure method and equal-pressure method are important and widely used methods in gas permeability testing of plastic film. Abundant data comparison in Labthink Labs has proved that these two methods are independent test methods and there is no linear relationship between them.
