1. Development of Sensor Method
Sensor method appears in the field of water vapor permeability testing in 1970s. With its development of more than 30 years, it has become an important method and has extensive applications. Before sensor method, weighing method is the only method in use. Generally, sensor method is divided into: infrared sensor method, dynamic relative humidity method and electrolyzing analysis method.
2. Infrared Sensor Method
Water vapor has specific absorption spectrum. Infrared sensor can test water vapor density by measuring energy lost of infrared when permeating through water vapor area. This method is named infrared sensor method.
Its testing principle is as follows (see Fig 1): testing chamber is divided into dry chamber and humidity chamber by specimen. The former maintains a stable (specified) and relatively lower humidity and the latter has a controlled humidity (100% RH), which forms stable humidity difference between the two chambers. Water vapor permeates through specimen from the controlled humidity chamber to dry chamber, and combines with dry gas in dry chamber. And then, it is carried by dry carrier gas to sensor. Infrared sensor can test the water vapor content in the dry carrier gas and output corresponding electric signal which correlates with humidity content. The stability of electronic signal is an indication that permeation has achieved a stable state; and now the mass of water vapor permeation and other indexes could be calculated according to electronic signal output by sensor.
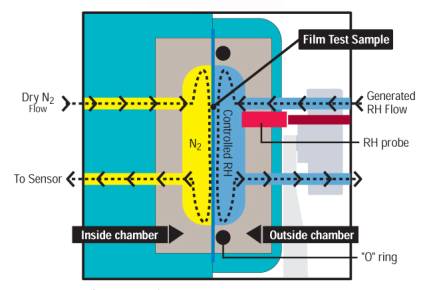
Fig.1 Principle of Infrared Testing Method
3. Electrolytic Method
Electrolytic cell sensor is designed on reaction characteristic of phosphorous pentoxide with water vapors. It contains two spiral wire electrodes, a thin layer of phosphorous pentoxide is mounted on the inside wall of glass capillary. The dry gas passes through the capillary where the moisture content is quantitatively absorbed by the phosphorous pentoxide and forms phosphoric acid, which is then decomposed electrolytically into hydrogen and oxygen by the application of a D.C. voltage of about 70V to the electrodes. Current flow is formed between electrodes. At the same time, phosphorous pentoxide will be regenerated. The mass of the moisture electrolyzed is calculated from the electrolytic current required. Electrolytic method is the one that employs electrolytic cell sensor to test specimen water vapor permeability.
Its testing principle is shown as follows (see Fig 2): the testing chamber is divided into a dry chamber and controlled humidity chamber with specimen. While the former maintains a stable (specified) and relatively lower humidity, the latter has a controlled humidity. Then the humidity difference, formed between two chambers, promotes water vapor permeating through specimen from the controlled humidity chamber to dry chamber to combine with dry gases in dry chamber and then it is carried by dry carrier gas to the sensor. Electrolytic cell sensor will test the water vapor content in the dry carrier gas and output corresponding electric signal. When the electric signal has become stable (an indication that permeation has achieved a stable state), the mass of water vapor permeation and other indexes could be calculated according to electronic signal output by sensor. Labthink TSY-W3 is the instrument for film water vapor permeability testing based on this method.
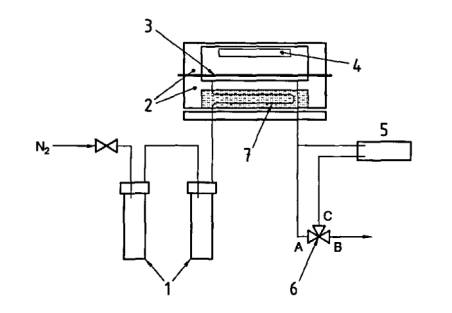
Fig 2 Testing Principle of Electrolytic Method
Note: 1. drying tube; 2. 2-chamber transmission chamber; 3. specimen; 4. glass fiberboard, (dipped in vitriol solution); 5. electrolytic cell; 6. conversion valve; 7. tube, used for supplying carrier gas (in the self temperature controlling liquid, gas temperature can be controlled at testing temperature)
4. Dynamic Relative Humidity Method
Dynamic relative humidity method employs humidity sensor that has very quick reaction towards humidity change and its testing principle is as follows (see Fig 3): the testing chamber is divided into dry chamber and controlled humidity chamber with specimen. With humidity controller, upper chamber is kept in dry environment and humidity chamber maintains humidity of 100%RH (normal). Since water vapor permeation increases the relative humidity of upper chamber, humidity sensor begins to analyze humidity change and monitors time required from min. value to max. value. Water vapor permeation indexes of specimen could be calculated by testing continuously, analyzing humidity curve and comparing standard electric signal. Generally, the humidity of dry chamber is 10% or 35%. Other humidity within calibration range is also adopted, min. and max. values of testing vary according to standards. For instance, ASTM E398-03 standard requires that humidity range of dry chamber is 10+0.1%RH or 35+0.1%RH, while in ISO 15106-1 standard it should be +1%RH or +2%RH. Labthink TSY-T2 is designed and manufactured according to dynamic relative humidity method.
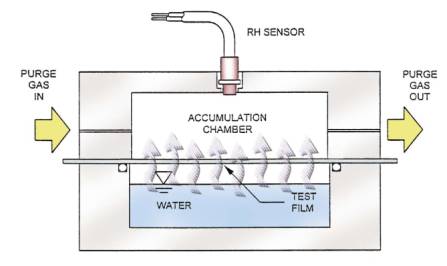
Fig 3 Principle of Dynamic Relative Humidity Method
5. Calculation of Testing Results
The amount of water vapor permeation cannot be tested directly by sensor method. Instead it is measured indirectly by testing and analyzing electric signal. Some standards clearly show that all sensors should calibrate reference film and specify calibration coefficient before testing. This is because the accuracy of reference film data will directly influence instrument accuracy. Reference film data is collected with cup method.
Some documents point out that sensor method is of high efficiency and precision. As a matter of fact, it depends on the precision and sensitivity of instrument. Instrument of sensor method could guarantee high efficiency and test material with high permeation in a short period, provided the sensor is excellent.
